Optimal Stopping - Look-then-Leap Rule and Practical Implementation with Java
In this article, we are going to dive into the what is the optimal stopping and we are going to write practical implementation with Java. First, …

Kadane’s algorithm could be a good solution to find maximum subarray in the given list. First let’s describe the maximum subarray problem.
Given an array, find the contiguous subarray with the largest sum.
For instance for this array:
int[] arr = {1, -3, 2, 1, -1};
// Solution is:
int[] result = {2, 1};
// Because [2,1] = 2+1=3 is the max sum
Now let’s clarify the what do we mean by subarray
Subarray is a slice of contiguous array that maintains the order of the elements. You would understand better with the example:
For the given array: {1, -3, 2, 1, -1}
{1} is a subarray (one element could be subarray also)
{1, -3} is a subarray
{1, -3, 2} is a subarray
{1, -3, -1}is not a subarray (because it is not contiguous)
We may use the brute force with two for loops. But it will take $O(n²)$ times which is not efficient
For instance, outer loop starts with index 0, then inner loop starts with index 1:
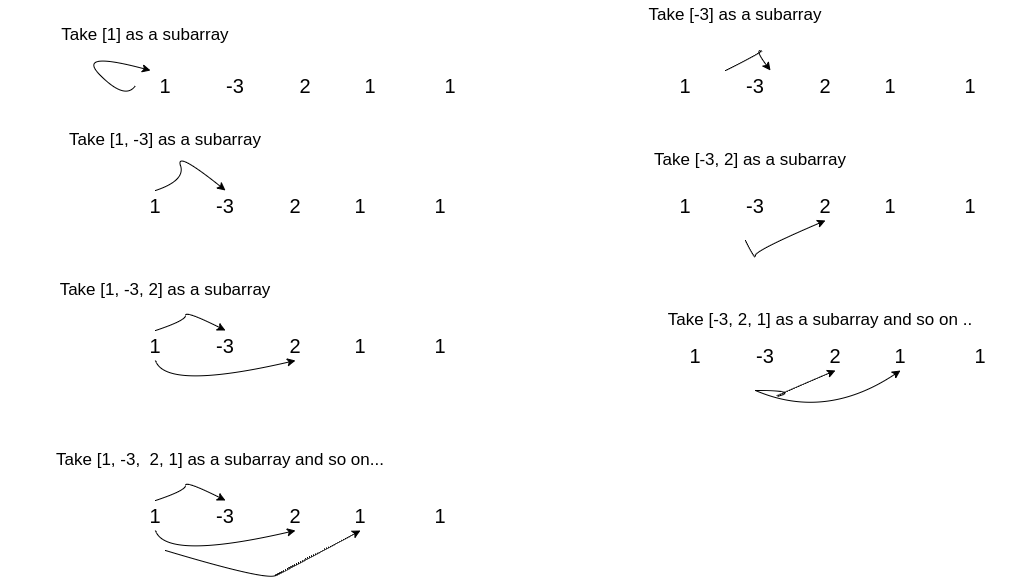
Instead of brute force solution we are going to find an answer what is the maximum subarray at ending index i ?
Here is the picture for the algorithm

Even idea is simple, it will take: $$ O(n²) $$
However, this algorithm can be enhanced and after that it takes only $$O(n)$$
Idea is to find local maximum subarray
At index i, local maximum subarray could be:
just current index itself [i]
or current element combined with the previous maximum subarray
For instance at index 2:
int[] arr = {1, -3, 2, 1, 1}; // index 2 = arr[2] = 2
At index 2, we can say that :
Maximum subarray can only contain subarray [2] whose sum is equal to 2
Or it can be combination of the maximum subarray at index 1 plus maximum subarray which only contains index 2 => [1, -3, 2]
After we check the both options we can update the maximum global subarray
We won’t apply this strategy for the first element, because it is unnecessary
Here is the pseudocode:
public static int kadane(int[] arr) {
max_local = max_global = arr[0];
for i from 1 to (size() - 1) {
max_local = max(arr[i], max_local + arr[i])
if (max_local > max_global) {
max_global = max_local;
}
}
return max_global;
}
import java.util.*;
public class KadaneAlgorithm {
public static int kadane(int[] arr) {
int max_local = arr[0];
int max_global = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
int maximumSubArrayAtIndex_i = arr[i];
int previousMaximumSubArray = max_local;
max_local = Math.max(maximumSubArrayAtIndex_i, previousMaximumSubArray + arr[i]);
if (max_local > max_global) {
max_global = max_local;
}
}
return max_global;
}
}

In this article, we are going to dive into the what is the optimal stopping and we are going to write practical implementation with Java. First, …
In distributed systems, we generally face the challenge of keeping our databases and external systems in sync. For instance when we create an order we …