In this post, I am going to explain some terms about stream processing and also terms used in Apache Flink
You may see the all my notes about Apache Flink with this link
State
- At a high level, we can consider state as memory in operators in Flink that remembers information about past input and can be used to influence the processing of future input.
- State is data information generated during computations that plays a very important role in fault tolerance, failure recovery and checkpoints in Apache Flink.
Operators
- Operators transform one or more data streams to another data streams (this could be the either same type of data stream of different type of data stream).
- A few operators form the dataflow graph which represent the program.
Dataflow Graphs
- A dataflow program describe how data flows between operations
- Dataflow program are commonly represented as directed graphs where nodes are called operators (represent computations) and edges represent data dependencies

Data Sources
- Operation without input ports are called data sources.
- A dataflow graph must have at least one data source
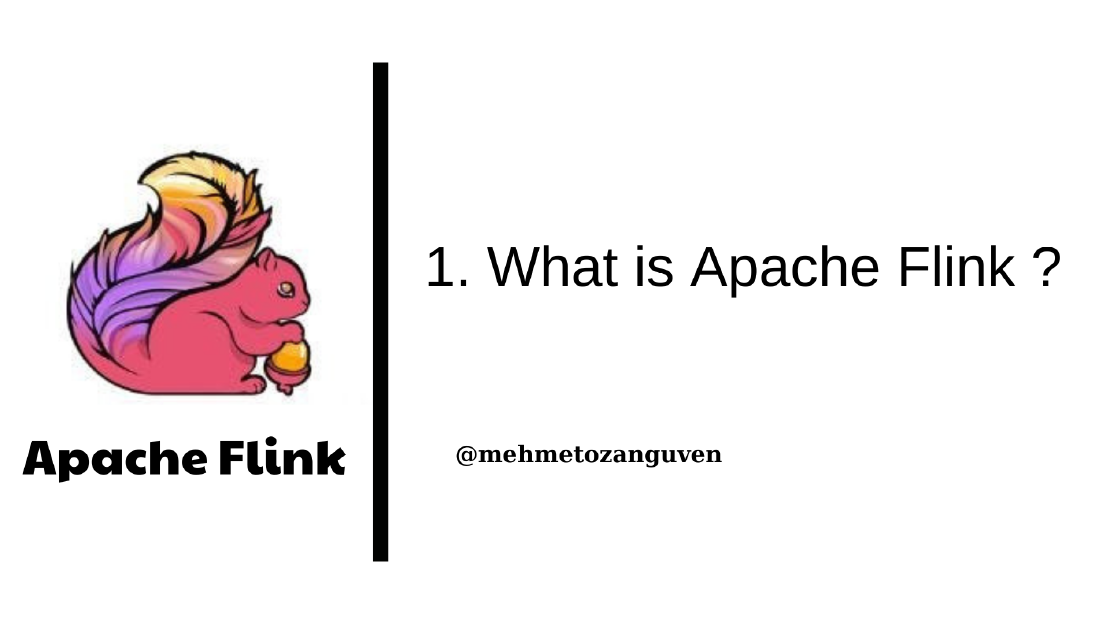
- In the DataFlow Graph, Tweet source is a data source for that dataflow.
Data Sinks
- Operation without output ports are called data sinks.
- A dataflow graph must have at least one data source.
- In the DataFlow Graph, Trending topics sink is a data sink for that dataflow.
Logical Dataflow(JobGraph) and Physical Dataflow(ExecutionGraph)
- Logical dataflow represent a high level view of the program. In logical dataflow the nodes are operators the edges indicate input/output-relationships or data streams or data sets.
- In order to execute a dataflow program, its logical graph is converted into a physical dataflow which specifies in detail how the program is executed.
- In physical dataflow graph, the nodes represent tasks.
Data Parallelism and Task Parallelism
- We can exploit parallelism in dataflow in different ways.
- Data parallelism: We divide our input data and we have tasks of the same operation execute on the data subsets in parallel.
- Using data parallelism we can process large volumes of data and spreading the computation load across several computing nodes
- Task parallelism: We can have tasks from different operators performing computations same or different data in parallel.
- Using task parallelism we can better utilize the computing resources of cluster.
Data Exchange Strategies
- Data exchange strategies define how the data items are assigned to tasks in a physical dataflow graph
- This strategy can be chosen automatically by the execution engine or explicitly imposed by the programmer.
- Here is the common data exchange strategies:
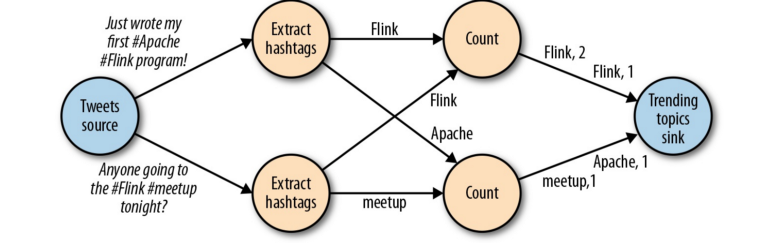
- Forward Strategy sends data from a task to a receiving task. If both tasks are located on the same physical machine(done by task schedulers), this exchange strategy avoids network communication.
- Broadcast Strategy sends every data item to all parallel tasks of an operator. Because this strategy replicates data and involves network communication, it is fairly expensive.
- Key-based Strategy divide data by a key attribute and guarantees that data items having the same key will be processed by the same tasks
- Random Strategy uniformly distributes data items to operator tasks in order to evenly distribute the load across computing tasks
Data ingestion and Data Egress
- They allow the stream processor to communicate with external systems.
- Data ingestion is the operation of fetching raw data from external sources and converting it into a format suitable for processing.
- Operators that implement data ingestion logic are called data sources.
- A data source can ingest data from a TCP socket, a file, a Kafka topic or a sensor data interface.
- Data egress is the operation of producing output in a form of suitable for consumption by external systems.
- Operators that perform data egress are called data sinks.
- Examples: files, databases, message queues and monitoring interfaces.
There is also “operations on data stream” such as window operations, transformation operations etc.. I am going to explain these operations in the later post(s)…
Note: If you want to see all terms about Apache Flink, you may go to the https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.10/concepts/glossary.html#Record